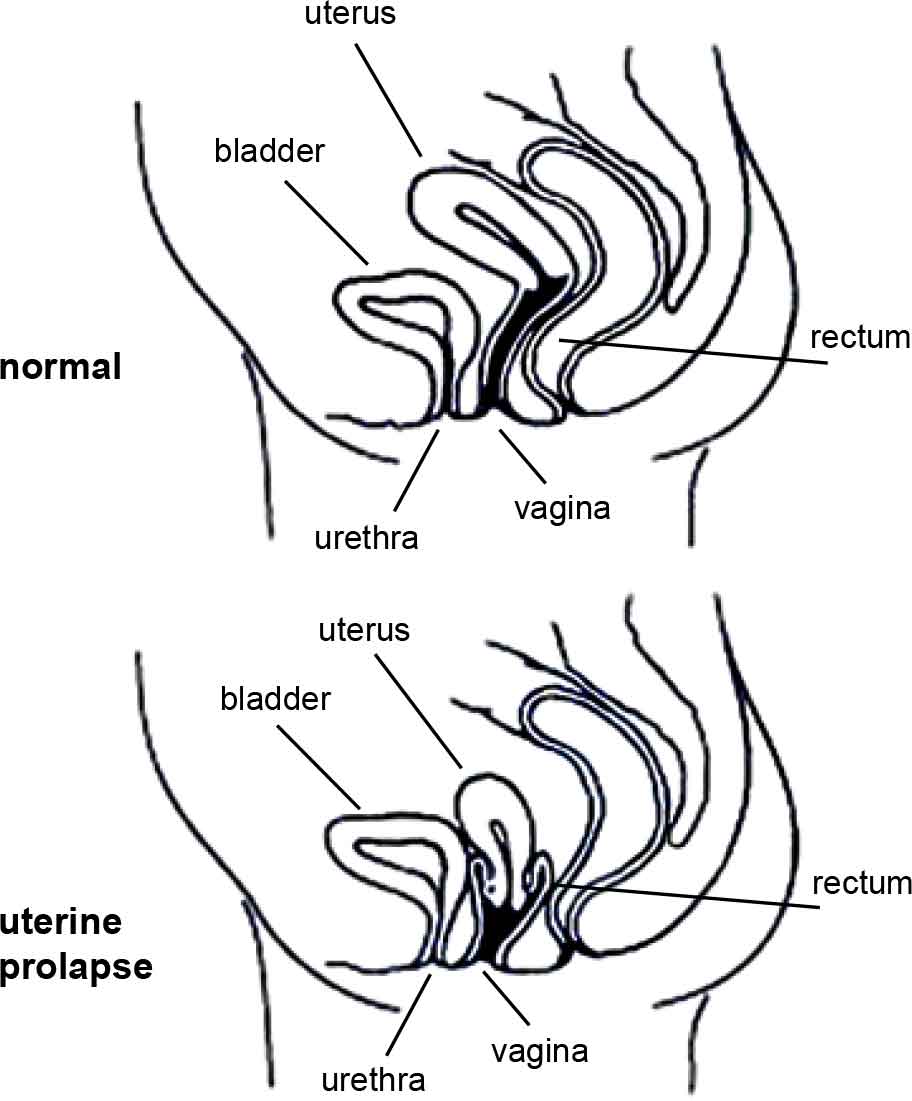
What is a vaginal (or pelvic organ) prolapse?Your pelvic organs include your bladder, uterus (womb) and rectum (back passage). These organs are held in place by tissues called “fascia” and “ligaments”. These tissues help to join your pelvic organs to the bony side walls of the pelvis and hold them inside your pelvis. Your pelvic floor muscles also hold up your pelvic organs from below. If the fascia and ligaments are torn or stretched for any reason, and if your pelvic floor muscles are weak, then your pelvic organs (your bladder, uterus, or rectum) might not be held in their right place and they may bulge down into the vagina (birth canal). |
Što je vaginalni prolaps (ili prolaps zdjeličnog organa)?Zdjelične organe čine: mokraćni mjehur, uterus (maternica) i rektum (čmar). Ove organe drže tkiva koja se zovu “fascia” i “ligamenti”. Ova tkiva vežu zdjelične organe uz koštane stijenke zdjelice i drže ih u zdjelici. Mišići dna zdjelice također drže zdjelične organe, s donje strane. Ukoliko se fascia i ligamenti iz bilo kojeg razloga poderu ili rastegnu, te ukoliko su vam mišići dna zdjelice oslabljeni, zdjelični organi (mjehur, uterus ili rektum) možda više nisu na svom mjestu i mogu se spustiti u vaginu (porođajni kanal). |
What are the signs of prolapse?There are a few signs that you may have a prolapse. These signs depend on the type of prolapse and how much pelvic organ support has been lost. Early on, you may not know you have a prolapse, but your doctor or nurse might be able to see your prolapse when you have your routine Pap test. When a prolapse is further down, you may notice things such as:
These signs can be worse at the end of the day and may feel better after lying down. If the prolapse bulges right outside your body, you may feel sore and bleed as the prolapse rubs on your underwear.
|
Koji su znakovi prolapsa?Nekoliko znakova može ukazivati da imate prolaps. Ovi znakovi ovise o tipu prolapsa i koliko je izgubljeno potpore zdjeličnih organa. Na samom početku možda nećete ni znati da imate prolaps, ali liječnik ili sestra može vidjeti prolaps prilikom redovitog Papa testa. Kada je prolaps dublji, možete primijetiti:
Ovi znakovi se mogu pogoršati pri kraju dana, a poboljšati kada legnete i odmorite se. Ako je prolaps izašao vani, možete imati bolove i krvarenje zbog trenja o donje rublje.
|
What causes prolapse?The pelvic organs are held inside the pelvis by strong healthy fascia. They are held up from below by pelvic floor muscles that work like a firm muscle sling. If the support tissues (fascia and ligaments) that keep the bladder, uterus and bowel in place inside the pelvis are weak or damaged, or if the pelvic floor muscles are weak and saggy, then prolapse can happen. Childbirth is the main cause of prolapse. On the way down the vagina, the baby can stretch and tear the support tissues and the pelvic floor muscles. The more vaginal births you have, the more likely you are to have a prolapse. |
Što uzrokuje prolaps?Zdjelične organe u zdjelici drži jaka zdrava fascia. Odozdo ih drže mišići dna zdjelice koji se ponašaju kao čvrsta mišićna ljuljačka. Ako su nosiva tkiva (fascia i ligamenti) koja drže mjehur, uterus i crijeva na svom mjestu u zdjelici slaba ili oštećena, ili ako su mišići dna zdjelice slabi i obješeni, može doći do prolapsa. Porođaj je najveći uzročnik prolapsa. Na svom putu kroz vaginu, beba može rastegnuti i poderati nosiva tkiva i mišiće dna zdjelice. Što imate veći broj vaginalnih porođaja, veća je mogućnost da ćete imati prolaps. |
|
|
|
|
Other things that press down on the pelvic organs and the pelvic floor muscles that can lead to prolapse, are:
|
Ostali uzročnici koji pritišću zdjelične organe i mišiće dna zdjelice i mogu dovesti do prolapsa, su:
|
Types of prolapsePelvic organs may bulge through the front wall of the vagina (called a cystocele [sist-o-seal]), through the back vaginal wall (called a rectocele [rec-to-seal] or an enterocele (enter-o-seal]) or the uterus may drop down into your vagina (uterine prolapse). More than one organ may bulge into the vagina. |
Tipovi prolapsaZdjelični organi mogu se izbočiti kroz prednju vaginalnu stijenku (koja se zove cistocela), kroz stražnju vaginalnu stijenku (koja se zove rektocela ili enterocela) ili se maternica može spustiti u vaginu (spuštena maternica). U vaginu se može spustiti više organa istovremeno. |
Who is likely to have a prolapse?Prolapse tends to run in families. It is more likely after menopause or if you are overweight. But it can happen in young women right after having a baby.
|
Kome prijeti opasnost od prolapsa?Prolaps može biti nasljedna pojava. Češće se javlja nakon menopauze ili kod prekomjerne težine. No, može se dogoditi i mlađim ženama neposredno nakon porođaja.
|
What can be done to help prevent prolapse?It is much better to prevent prolapse than try to fix it! If any women in your close family have had a prolapse, you are more at risk and you need to try very hard to follow the advice given here. As prolapse is due to weak pelvic tissues and pelvic floor muscles, you need to keep your pelvic floor muscles strong no matter what your age. Pelvic floor muscles can be made stronger with proper training (See the brochure “Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for Women”). It is important to have your pelvic floor muscle training checked by an expert such as a pelvic floor physiotherapist or a continence nurse advisor. If you have been told you have a prolapse, these experts are the best people to help plan a pelvic floor muscle training program to suit your needs. |
Štose može učiniti kako bi se spriječio prolaps?Puno je bolje spriječiti prolaps nego ga pokušati liječiti! Ako je neka žena iz vašeg bliskog rodbinskog kruga imala prolaps, vama prijeti veća opasnost i zato se morate strogo držati ovih savjeta. Kako prolaps nastaje zbog slabih zdjeličnih tkiva i mišića dna zdjelice, morate ojačati mišiće dna zdjelice, bez obzira koliko imate godina. Mišići dna zdjelice mogu se ojačati pravilnim vježbama (vidi brošuru “Vježbe za mišiće dna zdjelice za žene”). Važno je da vježbe mišića dna zdjelice provjeri neki stručnjak, kao što je fizioterapeut za dno zdjelice ili medicinska sestra koja je savjetnik za inkontinenciju. Ako vam je rečeno da imate prolaps, ovi stručnjaci su najbolje osobe koje vam mogu pomoći u planiranju programa vježbi mišića dna zdjelice koje odgovaraju vašim potrebama. |
What can be done to treat prolapse once it has happened?Prolapse can be dealt with simply or with surgery—it depends on the level of prolapse. The simple approach Prolapse can often be treated without surgery, chiefly in the early stages, and when the prolapse is mild. The simple approach can mean:
The surgery approach Surgery can be done to repair the torn or stretched fascia and ligaments. Surgery can be done through the vagina or the tummy. Sometimes special mesh is placed into the front or the back vaginal wall to strengthen it where it is weak or torn. As the body heals, the mesh helps form stronger tissues to give more support where it is needed. After surgery To prevent the prolapse coming back again, you should make sure you:
The diagrams have been reprinted with kind permission from Women’s Health Queensland Wide’s Genital Prolapse factsheet. |
Što se može učiniti za liječenje prolapsa koji se već dogodio?Prolaps se može rješavati najednostavan operacijomm—što ovisi o jačini prolapsa. Jednostavan pristup Prolaps se često može liječiti bez operacije, uglavnom u ranim fazama te ako se radi o blažem prolapsu. Jednostavan pristup znači:
Operativni zahvat Operativno se mogu popraviti poderana ili razvučena fascia i ligamenti. Operacija se može uraditi vaginalno ili kroz trbuh. U nekim slučajevima se stavi posebna mreža u prednju ili zadnju vaginalnu stijenku radi ojačanja, tamo gdje je slaba i poderana. Kako se tijelo oporavlja, mreža pomaže stvaranju jačih tkiva koja će dati bolju potporu gdje je potrebna. Nakon operacije Da biste spriječiti ponovni prolaps, morate obvezno:
Grafički prikazi su preslikani iz brošure Wide’s Genital Prolapse uz odobrenje Women’s Health Queensland |
Seek helpQualified nurses are available if you call the National Continence Helpline on 1800 33 00 66* (Monday to Friday, between 8.00am to 8.00pm Australian Eastern Standard Time) for free:
If you have difficulty speaking or understanding English you can access the Helpline through the free Telephone Interpreter Service on 13 14 50. The phone will be answered in English, so please name the language you speak and wait on the phone. You will be connected to an interpreter who speaks your language. Tell the interpreter you wish to call the National Continence Helpline on 1800 33 00 66. Wait on the phone to be connected and the interpreter will assist you to speak with a continence nurse advisor. All calls are confidential. * Calls from mobile telephones are charged at applicable rates. |
Potražite pomoćDostupne su vam stručne medicinske sestre ako nazovete Nacionalnu liniju za pomoć zbog inkontinencije na 1800 33 00 66* (od ponedjeljka do petka, između 8.00h i 20.00h po standardnom istočnom australskom vremenu) za besplatne:
Ako imate problema u razgovoru ili razumijevanju engleskog jezika, možete nazvati Liniju za pomoć (Helpline) putem besplatne Telefonske službe tumača na 13 14 50. Na poziv ćete dobit odgovor na engleskom jeziku, pa recite jezik koji govorite i čekajte na liniji. Bit ćete spojeni s tumačem koji govori vaš jezik. Recite tumaču da želite razgovarati s National Continence Helpline na 1800 33 00 66. Pričekajte na liniji da budete spojeni i tumač će vam pomoći u razgovoru s medicinskom sestrom, savjetnikom za inkontinenciju. Svi razgovori su povjerljivi. * Pozivi s mobitela naplaćuju se po važećim cijenama. |
Prolapse in Croatian
Prolaps
Browse and download our factsheets in Croatian
Last Updated: Fri 30, Jul 2021
Last Reviewed: Tue 17, Mar 2020