What is a vaginal (or pelvic organ) prolapse?Your pelvic organs include your bladder, uterus (womb) and rectum (back passage). These organs are held in place by tissues called “fascia” and “ligaments”. These tissues help to join your pelvic organs to the bony side walls of the pelvis and hold them inside your pelvis. Your pelvic floor muscles also hold up your pelvic organs from below. If the fascia and ligaments are torn or stretched for any reason, and if your pelvic floor muscles are weak, then your pelvic organs (your bladder, uterus, or rectum) might not be held in their right place and they may bulge down into the vagina (birth canal). |
X’inhu l-prolass vaġinali (jew -organi tal-pelvi)?L-organi tiegħek tal-pelvi jinkludu l-bużżieqa tal-awrina, l-utru (il-ġuf) u r-rektum (il-passaġġ ta’ wara) tiegħek. Dawn l-organi jinżammu f’posthom permezz ta’ tessuti magħrufa bħala “fascia” u “ligamenti”. Dawn it-tessuti jgħinu biex jgħaqqdu l-organi tiegħek tal-pelvi mal-ħitan tal-ġnub mgћaddma tal-pelvi u jżommuhom ġewwa l-pelvi tiegħek. Il-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi tiegħek iżommu wkoll ‘il fuq l-organi tal-pelvi tiegħek minn taħt. Jekk il-fascia u ligamenti jiċċartu jew jinġebdu għal kwalunkwe raġuni, u jekk il-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi tiegħek huma dgħajfa, allura l-organi tal-pelvi tiegħek (il-bużżieqa tal-awrina, l-utru, jew ir-rektum tiegħek) jistgħu ma jkunux miżmuma fejn suppost ikunu, u dawn jistgħu jiżżaqqu ‘l isfel fil-vaġina (kanal tat-twelid). |
What are the signs of prolapse?There are a few signs that you may have a prolapse. These signs depend on the type of prolapse and how much pelvic organ support has been lost. Early on, you may not know you have a prolapse, but your doctor or nurse might be able to see your prolapse when you have your routine Pap test. When a prolapse is further down, you may notice things such as:
These signs can be worse at the end of the day and may feel better after lying down. If the prolapse bulges right outside your body, you may feel sore and bleed as the prolapse rubs on your underwear.
|
X’inhuma s-sinjali tal-prolass?Hemm xi ftit sinjali li juru li inti jista’ jkollok prolass. Dawn is-sinjali jiddependu mit-tip ta’ prolass u kemm intilef sapport tal-organu tal-pelvi.Għall-ewwel, għandu mnejn ma tkunx taf li għandek prolass, iżda it-tabib jew in-ners tiegħek jistgħu jkunu kapaċi jaraw il-prolass tiegħek meta tagħmel il-Pap test tiegћek tas-soltu. Meta l-prolass ikun aktar ‘l isfel, int għandek mnejn tinnota ċerti affarijiet bħal:
Dawn is-sinjali jistgħu jkunu agħar fi tmiem il-jum u tista’ tħossok aħjar wara li timtedd. Jekk il-prolass jisporġi ‘l barra ġismek, int tista’ tħossok muġugħa u joħroġlok id-demm hekk kif il-prolass iħokk mal-qalziet ta’ taħt tiegħek.
|
What causes prolapse?The pelvic organs are held inside the pelvis by strong healthy fascia. They are held up from below by pelvic floor muscles that work like a firm muscle sling. If the support tissues (fascia and ligaments) that keep the bladder, uterus and bowel in place inside the pelvis are weak or damaged, or if the pelvic floor muscles are weak and saggy, then prolapse can happen. Childbirth is the main cause of prolapse. On the way down the vagina, the baby can stretch and tear the support tissues and the pelvic floor muscles. The more vaginal births you have, the more likely you are to have a prolapse. |
X’inhuma l-kawżi tal-prolass?L-organi tal-pelvi jinżammu ġewwa l-pelvi permezz ta’ fascia b’saħħitha. Huma jinżammu ‘l fuq minn naћa t’isfel permezz tal-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi li jaħdmu bħala branda iebsa tal-muskoli. Jekk it-tessuti tas-sapport (fascia u ligamenti) li jżommu l-bużżieqa tal-awrina, l-utru, u l-imsaren f’posthom ġewwa l-pelvi huma dgħajfin jew sofrew xi ħsara, jew jekk il-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi huma dgħajfa u mżaqqa, allura jista’ jkollok prolass. It-twelid hi r-raġuni prinċipali tal-prolass. Hekk kif tkun nieżla fil-vaġina, it-tarbija tista’ tistira u ċċarrat it-tessuti ta’ sapport u l-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi. Aktar ma jkollok drabi ta’ twelid vaġinali, aktar ikun hemm probabbilità li ser ikollok prolass. |
 |
 |
|
Other things that press down on the pelvic organs and the pelvic floor muscles that can lead to prolapse, are:
|
Affarijiet oħra li jagħfsu ‘l isfel fuq l-organi tal-pelvi u l-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi li jistgħu jwasslu għal prolass, huma:
|
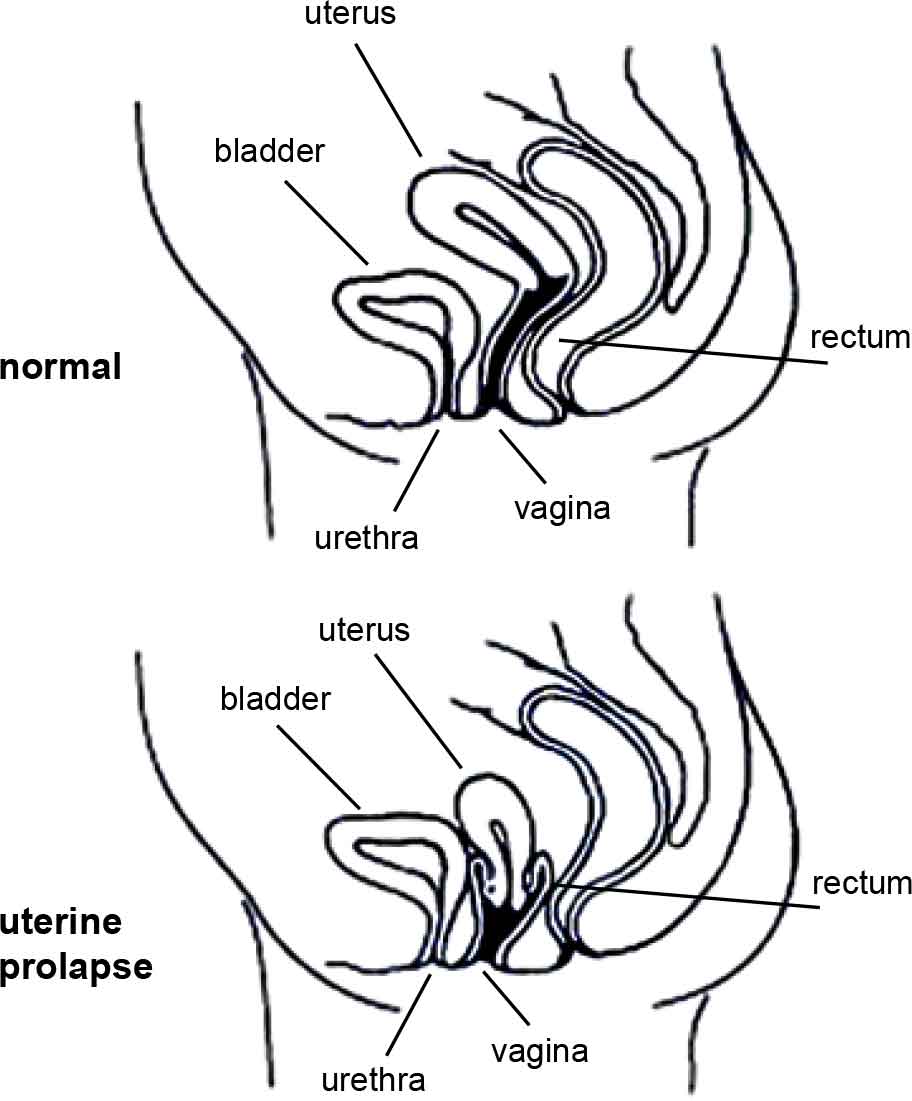
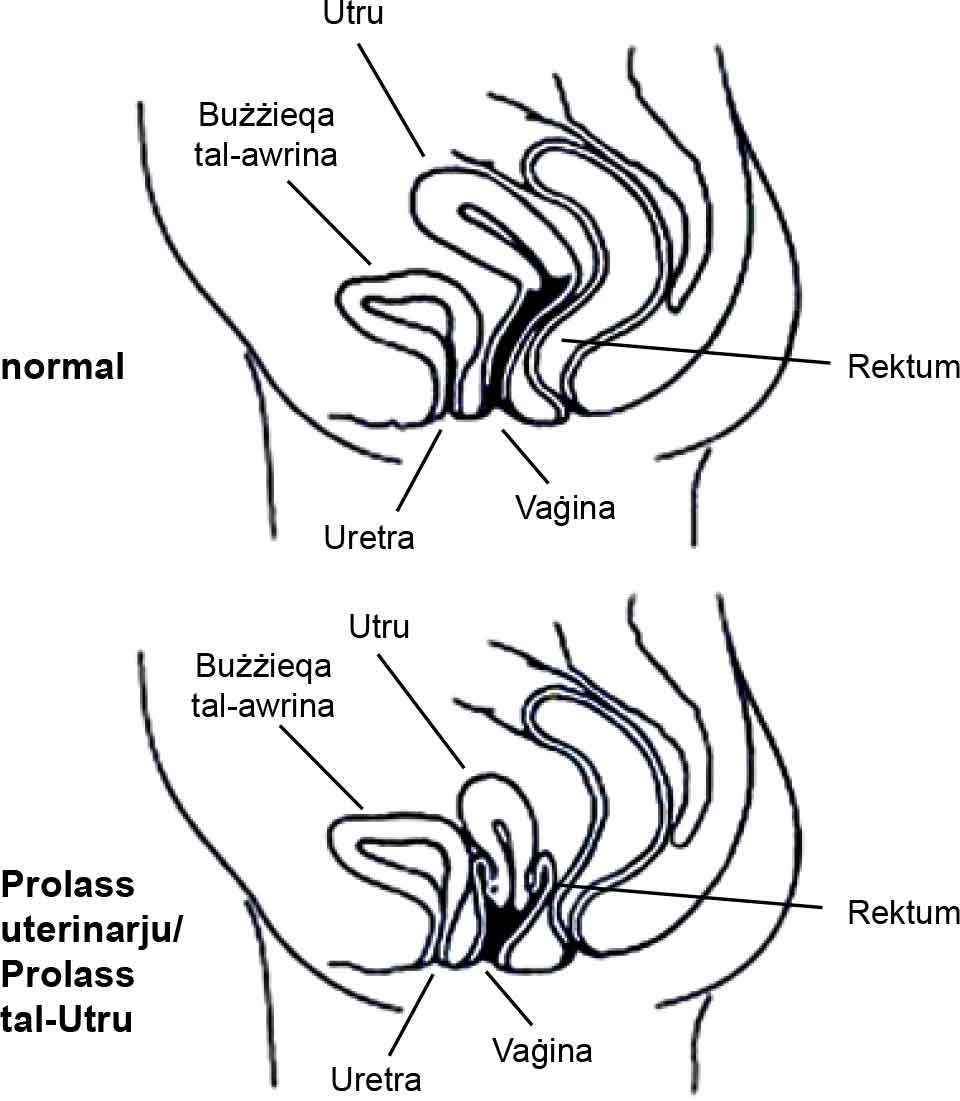
Types of prolapsePelvic organs may bulge through the front wall of the vagina (called a cystocele [sist-o-seal]), through the back vaginal wall (called a rectocele [rec-to-seal] or an enterocele (enter-o-seal]) or the uterus may drop down into your vagina (uterine prolapse). More than one organ may bulge into the vagina. |
Tipi ta’ prolassL-organi tal-pelvi jistgħu jisporġu minn ġol-ħajt ta’ quddiem tal-vaġina (magħrufa bħala ċistoċeli [sist-o-siġill]), minn ġol-ħajt ta’ wara tal-vaġina (magħruf bħala rektoċeli [rec għall-siġill] jew enteroċeli (enter-o-siġill) jew l-utru jista’ jinżel l-isfel fil-vaġina tiegħek (prolass uterin). Jista’ jkun hemm aktar minn organu wieħed li jisporġi fil-vaġina. |
Who is likely to have a prolapse?Prolapse tends to run in families. It is more likely after menopause or if you are overweight. But it can happen in young women right after having a baby.
|
Min x’aktarx ikollu prolass?Il-prolass għandu ħabta jkun ereditarju. Hemm probabbilità akbar li jiġri wara menopawsa jew jekk tiżen aktar milli suppost. Imma nisa żgħażagħ jista’ jkollhom dan dritt wara li jkollhom tarbija.
|
What can be done to help prevent prolapse?It is much better to prevent prolapse than try to fix it! If any women in your close family have had a prolapse, you are more at risk and you need to try very hard to follow the advice given here. As prolapse is due to weak pelvic tissues and pelvic floor muscles, you need to keep your pelvic floor muscles strong no matter what your age. Pelvic floor muscles can be made stronger with proper training (See the brochure “Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for Women”). It is important to have your pelvic floor muscle training checked by an expert such as a pelvic floor physiotherapist or a continence nurse advisor. If you have been told you have a prolapse, these experts are the best people to help plan a pelvic floor muscle training program to suit your needs. |
X’jista’ jsir biex iservi ta’ għajnuna ħalli l-prolass ma jiġrix?Huwa ferm aħjar li tevita l-prolass milli tipprova ssewwih! Jekk xi nisa fil-familja li tiġi minnek kellha prolass, inti tinsab f’riskju akbar u trid tagħmel l-almu tiegħek kollu biex issegwi l-parir mogħti hawn. Peress li l-prolass huwa dovut għal tessuti tal-pelvi u muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi dgħajfa, int trid iżomm il-muskoli tiegħek tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi b’saħħithom hi x’inhi l-età tiegħek. Il-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi jistgħu jissaħħu permezz ta’ eżerċizzji tajba (Ara l-fuljett “Eżerċizzji tal-Muskoli tal-Qiegħ tal-Pelvi għan-Nisa”). Huwa importanti li tara li l-eżerċizzji tal-muskoli tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi tiegħek jkunu ċċekkjati minn espert bħal fiżjoterapista tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi jew ners konsulent tal-kontinenza. Jekk qalulek li għandek xi prolass, dawn l-esperti huma l-aħjar nies biex jgħinuk tippjana programm tal-eżerċizzju tal-muskolu tal-qiegħ tal-pelvi li jkun jgħodd għalik. |
What can be done to treat prolapse once it has happened?Prolapse can be dealt with simply or with surgery—it depends on the level of prolapse. The simple approach Prolapse can often be treated without surgery, chiefly in the early stages, and when the prolapse is mild. The simple approach can mean:
The surgery approach Surgery can be done to repair the torn or stretched fascia and ligaments. Surgery can be done through the vagina or the tummy. Sometimes special mesh is placed into the front or the back vaginal wall to strengthen it where it is weak or torn. As the body heals, the mesh helps form stronger tissues to give more support where it is needed. After surgery To prevent the prolapse coming back again, you should make sure you:
The diagrams have been reprinted with kind permission from Women’s Health Queensland Wide’s Genital Prolapse factsheet. |
X’jista’ jsir biex tikkura l-prolass ġaladarba jiġri dan?Il-prolass jista’ jiġi kkurat b’modsempliċijew permezz ta’ operazzjoni- jiddependi mill-livell tal-prolass. L-approċċ sempliċi Spiss il-prolass jista’ jiġi kkurat mingħajr operazzjoni, b’mod partikolari, fl-istadji bikrija, u meta l-prolass huwa moderat. L-approċċ sempliċi jista’ jfisser:
L-approċċ tal-operazzjoni Tista’ ssir operazzjoni biex jissewew il-fascia jew il- ligamenti mċarrta jew miġbuda. L-operazzjoni tista’ ssir minn ġol-vaġina jew minn ġoż-żaqq. Xi kultant titpoġġa mesh speċjali quddiem jew wara l-ħajt tal-vaġina biex tissaћћaћ fejn hi dgħajfa jew imqatta’. Hekk kif il-ġisem ifieq, il-mesh ser tgħin biex tifforma tessuti aktar b’saħħithom biex tagħti aktar sapport fejn ikun meħtieġ. Wara l-operazzjoni Biex tara li ma jerġax ikollok il-prolass, int għandek tara li int:
Id-dijagrammi ġew stampati mill-ġdid bil-permess ġentili mill-karta tal-fatti tal-Women’s Health Queensland Wide’s Genital Prolapse. |
Seek helpQualified nurses are available if you call the National Continence Helpline on 1800 33 00 66* (Monday to Friday, between 8.00am to 8.00pm Australian Eastern Standard Time) for free:
If you have difficulty speaking or understanding English you can access the Helpline through the free Telephone Interpreter Service on 13 14 50. The phone will be answered in English, so please name the language you speak and wait on the phone. You will be connected to an interpreter who speaks your language. Tell the interpreter you wish to call the National Continence Helpline on 1800 33 00 66. Wait on the phone to be connected and the interpreter will assist you to speak with a continence nurse advisor. All calls are confidential. * Calls from mobile telephones are charged at applicable rates. |
Itlob l-għajnunaHemm nersis ikkwalifikati jekk iċċempel lin-National Continence Helpline fuq 1800 33 00 66* (mit-Tnejn sal-Ġimgħa, bejn it-8.00am to 8.00pm AEST (Ħin Standard tal-Lvant tal-Awstralja)) mingħajr ħlas:
Jekk ikollok diffikulta’ biex titkellem jew biex tifhem bl-Ingliż jista’ jkollok aċċess għall-Helpline permezz tat-Telephone Interpreter Service fuq 13 14 50 b’xejn. It-telefon ikun imwieġeb bl-Ingliż, għalhekk għid liema lingwa titkellem u stenna fuq it-telefon. Tkun ikkonnettjat/a ma’ interpretu li jitkellem il-lingwa tiegħek. Għid lill-interpretu li tixtieq li ċċempel lin-National Continence Helpline fuq 1800 33 00 66. Stenna fuq it-telefon biex tkun ikkonnettjat/a u l-interpretu jgħinek biex titkellem ma’ ners li tagħti pariri dwar il-kontinenza. It-telefonati kollha huma konfidenzjali. * Telefonati minn fuq telefonijiet mowbajl ikunu ċċarġjati r-rati li japplikaw. |
Prolapse in Maltese
Prolass
Browse and download our factsheets in Maltese
Last Updated: Fri 30, Jul 2021
Last Reviewed: Tue 17, Mar 2020

