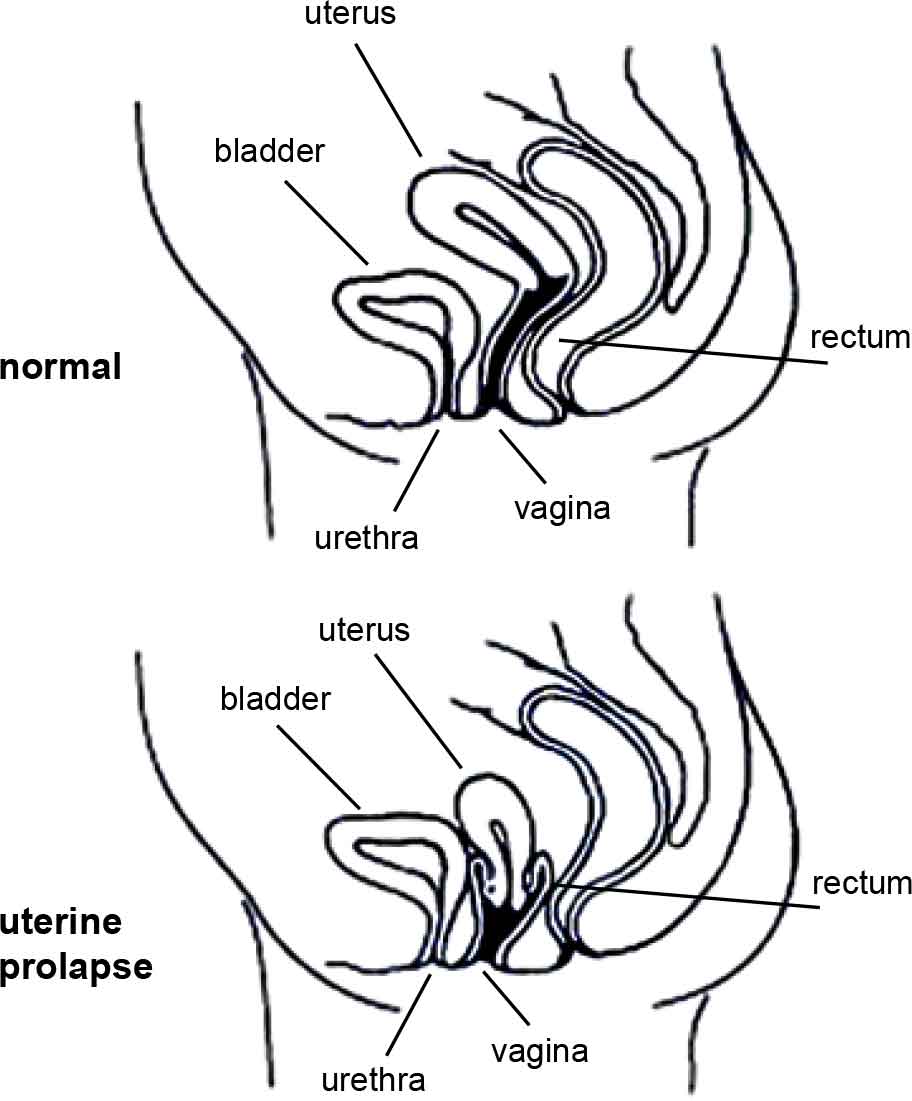
What is a vaginal (or pelvic organ) prolapse?Your pelvic organs include your bladder, uterus (womb) and rectum (back passage). These organs are held in place by tissues called “fascia” and “ligaments”. These tissues help to join your pelvic organs to the bony side walls of the pelvis and hold them inside your pelvis. Your pelvic floor muscles also hold up your pelvic organs from below. If the fascia and ligaments are torn or stretched for any reason, and if your pelvic floor muscles are weak, then your pelvic organs (your bladder, uterus, or rectum) might not be held in their right place and they may bulge down into the vagina (birth canal). |
ما هو التدلي المهبلي (أو تدلي أعضاء الحوض)؟تشمل الأعضاء الموجودة في الحوض المثانة، الرحم، والمستقيم. وتبقي على هذه الأعضاء في مكانها أنسجة تعرف باسم “الأربطة” و “لفافات”، وهي تساعد على توصيل الأعضاء الموجودة داخل الحوض مع جدرانه العظمية والإبقاء عليها بداخله. كما وتقوم عضلات قاع الحوض أيضا بسند الأعضاء الموجودة داخل الحوض من تحت. فإذا تمزقت الأربطة واللفافات أو تمطت لسبب ما، وكانت عضلات قاع الحوض لديك ضعيفة، فإن أعضاء الحوض (مثانتك ورحمك والمستقيم) قد لا تكون مثبتة في مكانها وبالتالي تنتؤ نحو الأسفل داخل المهبل. |
What are the signs of prolapse?There are a few signs that you may have a prolapse. These signs depend on the type of prolapse and how much pelvic organ support has been lost. Early on, you may not know you have a prolapse, but your doctor or nurse might be able to see your prolapse when you have your routine Pap test. When a prolapse is further down, you may notice things such as:
These signs can be worse at the end of the day and may feel better after lying down. If the prolapse bulges right outside your body, you may feel sore and bleed as the prolapse rubs on your underwear.
|
ما هي علامات تدلي عضو الحوض؟هناك بعض العلامات القليلة التي تشير إلى احتمال حدوث تدلي عضو الحوض لديك. وتعتمد هذه العلامات على نوع التدلي ومدى فقدان الدعم لأعضاء الحوض. وقد لا تكونين مدركة بأنك تعانين من التدلي في بدايته، إلا أن بإمكان طبيبك أو الممرضة رؤيته عند قيامهم بفحص المهبل الروتيني. أما بعد أن يزداد تدلي الأعضاء إلى الأسفل، فقد تلاحظين أمورا مثل:
ويمكن أن تزداد هذه العلامات سوءً في نهاية النهار، يليها تحسن بعد رقودك لفترة. إذا كان التدلي خارج الجسم، فقد تشعرين بالألم وتنزفين عند احتكاك الأعضاء المتدلية بملابسك الداخلية.
|
What causes prolapse?The pelvic organs are held inside the pelvis by strong healthy fascia. They are held up from below by pelvic floor muscles that work like a firm muscle sling. If the support tissues (fascia and ligaments) that keep the bladder, uterus and bowel in place inside the pelvis are weak or damaged, or if the pelvic floor muscles are weak and saggy, then prolapse can happen. Childbirth is the main cause of prolapse. On the way down the vagina, the baby can stretch and tear the support tissues and the pelvic floor muscles. The more vaginal births you have, the more likely you are to have a prolapse. |
ما الذي يتسبب في تدلي أعضاء الحوض؟تُبقي اللفافات الصحيحة القوية على أعضاء الحوض في مكانها، بينما تسندها من الأسفل عضلات قاع الحوض التي تقوم بدور مقلاع عضلي صلب. في الحالات التي تكون فيها الأنسجة الداعمة (الأربطة واللفافات) التي تُبقي على المثانة والرحم والمستقيم في مكانها ضعيفة أو مصابة بضرر، أو كانت عضلات قاع الحوض ضعيفة مترهلة، فقد يحدث تدلي لأعضاء الحوض. الولادة هي من أهم أسباب التدلي، لأن الجنين في طريقه إلى الأسفل عبر عنق الرحم يمكن أن يمط الأنسجة الداعمة وعضلات قاع الحوض ويمزقها. وكلما ارتفع عدد الولادات الطبيعية للمرأة كلما ارتفع احتمال إصابتها بتدلي أعضاء الحوض. |
|
|
|
|
Other things that press down on the pelvic organs and the pelvic floor muscles that can lead to prolapse, are:
|
ومن ضمن الأمور الأخرى التي تضغط على أعضاء الحوض وعضلات قاع الحوض وبالتالي قد تؤدي إلى الإصابة بتدليها هي:
|
Types of prolapsePelvic organs may bulge through the front wall of the vagina (called a cystocele [sist-o-seal]), through the back vaginal wall (called a rectocele [rec-to-seal] or an enterocele (enter-o-seal]) or the uterus may drop down into your vagina (uterine prolapse). More than one organ may bulge into the vagina. |
أنواع تدلي أعضاء الحوضيمكن أن تنتأ أعضاء الرحم عبر الجدار الأمامي للمبهل (ويعرف ذلك باسم القيلة المثانية)، أو عبر الجدار الخلفي للمهبل (ويعرف ذلك باسم فتق المستقيم أو القيلة المعوية) أو قد يهبط الرحم إلى داخل المهبل (تدلي الرحم). كما ويمكن لأكثر من عضو واحد أن ينتأ داخل المهبل. |
Who is likely to have a prolapse?Prolapse tends to run in families. It is more likely after menopause or if you are overweight. But it can happen in young women right after having a baby.
|
عند من يشيع حدوث تدلي أعضاء الحوض؟تدلي الحوض يميل إلى أن يكون وراثيا، وحصوله أكثر احتمالا بعد الإياس أو إذا كانت المرأة بدينة، إلا أنه قابل للحدوث عند النساء الشابات بمجرد ولادتهن لطفل.
|
What can be done to help prevent prolapse?It is much better to prevent prolapse than try to fix it! If any women in your close family have had a prolapse, you are more at risk and you need to try very hard to follow the advice given here. As prolapse is due to weak pelvic tissues and pelvic floor muscles, you need to keep your pelvic floor muscles strong no matter what your age. Pelvic floor muscles can be made stronger with proper training (See the brochure “Pelvic Floor Muscle Training for Women”). It is important to have your pelvic floor muscle training checked by an expert such as a pelvic floor physiotherapist or a continence nurse advisor. If you have been told you have a prolapse, these experts are the best people to help plan a pelvic floor muscle training program to suit your needs. |
ما هي طرق الوقاية من تدلي أعضاء الحوض؟من الأفضل بكثير الوقاية من تدلي أعضاء الحوض بدلا من محاولة تصحيحه! إذا كان أي من النساء في أسرتك مصاب بتدلي أعضاء الحوض، فأنت أكثر عرضة له وبالتالي عليك المحاولة جاهدة اتباع النصائح الواردة أدناه. يحدث تدلي أعضاء الحوض نتيجة ضعف أنسجة الحوض وعضلات قاع الحوض، وبالتالي عليك الإبقاء على تلك العضلات قوية بغض النظر عن سنك. يمكن تقوية عضلات قاع الحوض من خلال التمارين المناسبة لذلك (الرجاء مراجعة نشرة “تمارين عضلات قاع الحوض للنساء”). من المهم أن يقوم خبير مثل أخصائي العلاج الطبيعي أو ممرضة احتباس متخصصين بمراجعة تمارين عضلات قاع الحوض التي تقومين بها. إذا عرفت بأنك تعانين من تدلي أعضاء الحوض، فإن هؤلاء الخبراء هم أمثل من يساعدك في التخطيط لبرنامج تدريب عضلات قاع الحوض بحيث يناسب احتياجاتك. |
What can be done to treat prolapse once it has happened?Prolapse can be dealt with simply or with surgery—it depends on the level of prolapse. The simple approach Prolapse can often be treated without surgery, chiefly in the early stages, and when the prolapse is mild. The simple approach can mean:
The surgery approach Surgery can be done to repair the torn or stretched fascia and ligaments. Surgery can be done through the vagina or the tummy. Sometimes special mesh is placed into the front or the back vaginal wall to strengthen it where it is weak or torn. As the body heals, the mesh helps form stronger tissues to give more support where it is needed. After surgery To prevent the prolapse coming back again, you should make sure you:
The diagrams have been reprinted with kind permission from Women’s Health Queensland Wide’s Genital Prolapse factsheet. |
كيف يمكن معالجة تدلي أعضاء الحوض عندما يحدث؟يمكن معالجة تدلي أعضاء الحوضببساطةمن خلالالجراحة – ويتوقف ذلك على مستوى التدلي. الحل البسيط يمكن معالجة تدلي أعضاء الحوض في كثير من الحالات بالجراحة، خاصة في مراحله المبكرة، وعندما يكون التدلي بسيطا. ويعني الحل البسيط:
الحل بواسطة الجراحة يمكن إجراء الجراحة لتصحيح اللفافات أو الأربطة الممطوطة أو الممزقة، ويمكن إجرائها عبر المهبل أو البطن. في بعض الحالات يتم تركيب شبكة داخل الجدار الأمامي أو الخلفي للمهبل لتقويته في الأماكن التي يكون ممزقا أو ضعيفا فيها. ومع شفاء الجسم تساعد هذه الشبكة على تكوين أنسجة أقوى تعطي دعما أكبر حيث الحاجة إليه. بعد الجراحة لمنع حصول تدلي أعضاء الحوض مرة أخرى، عليك التأكد من القيام بالتالي:
تم نسخ الرسوم بإذن من صحيفة الحقائق عن تدلي الأعضاء التناسلية الصادرة عن هيئة صحة النساء في ولاية كوينزلاند. |
Seek helpQualified nurses are available if you call the National Continence Helpline on 1800 33 00 66* (Monday to Friday, between 8.00am to 8.00pm Australian Eastern Standard Time) for free:
If you have difficulty speaking or understanding English you can access the Helpline through the free Telephone Interpreter Service on 13 14 50. The phone will be answered in English, so please name the language you speak and wait on the phone. You will be connected to an interpreter who speaks your language. Tell the interpreter you wish to call the National Continence Helpline on 1800 33 00 66. Wait on the phone to be connected and the interpreter will assist you to speak with a continence nurse advisor. All calls are confidential. * Calls from mobile telephones are charged at applicable rates. |
احصل على المساعدةتتوفر ممرضات مؤهلات اذا اتصلت على خط المساعدة الوطني لشؤون الاحتباس على الرقم 1800 33 00 66 من الساعة 8 صباحاَ حتى 8 مساءاَ في توقيت الاسترالي الشرقي مجاناَ.
إذا كان لديك أي صعوبات اللغة الإنجليزية يمكنك الاتصال بخط المساعدة باستخدام خدمة الترجمة الهاتفية. اتصل بالرقم 13 14 50. في البداية سوف يرد عليك شخص يتكلم باللغة الإنجليزية، اذكر لغتك وانتظر على الهاتف. وسوف يتم تحويلك لمترجم يتحدث لغتك، أخبره عندها أنك تريد الاتصال بخط المساعدة الوطني لشؤون الاحتباس على الرقم 1800 33 00 66. انتظر على الهاتف وسوف يقوم المترجم بمساعدتك على التحدث مع ممرضة الاحتباس. وتقدم خدمات. جميع المكالمات سرية. * يتم حساب المكالمات من الهواتف المحمولة بالتسعيرة المفروضة عليها. |
Prolapse in Arabic
تدلي عضو الحوض
Browse and download our factsheets in Arabic
Last Updated: Fri 30, Jul 2021
Last Reviewed: Tue 17, Mar 2020